AWS Pricing for Beginners: How to Save on Your Cloud Bill

AWS offers a vast array of services with flexible pricing models, making it accessible for businesses of all sizes. But if you’re new to cloud computing, navigating AWS pricing can be daunting. This guide breaks down AWS pricing basics and shares practical tips to help you save on your cloud bill without sacrificing performance.
Understanding AWS Pricing Models
AWS pricing can be flexible and complex, but it’s primarily built around three main models:
-
— Pay-as-you-go: You only pay for what you use. This is the most common AWS pricing model and applies to many services, including EC2 (Elastic Compute Cloud) and S3 (Simple Storage Service).
-
— Save When You Reserve: You can save by committing to a service for a certain period (typically 1 to 3 years) and choosing Reserved Instances or Savings Plans, which offer discounts for long-term use.
-
— Pay Less with Volume-Based Discounts: As your usage increases, AWS may reduce your costs with volume discounts, especially for storage services like S3.
Key Tips to Save on AWS Costs
1. Choose the Right Instance Types
AWS offers different types of EC2 instances for specific workloads, such as General Purpose, Compute Optimized, and Memory Optimized instances. Choosing the right instance type for your workload helps avoid overpaying for resources you don’t need.
- — Tip: Start small and adjust as needed. For example, if you only need a basic server for a small website, choose a t3.micro instance instead of a larger instance.
2. Use the Free Tier Wisely
AWS offers a Free Tier that allows new users to try many services for free within specific limits for 12 months. Some services even offer Always Free usage options, such as AWS Lambda and DynamoDB, within certain limits.
- — Tip: Use the Free Tier to experiment, but be mindful of usage limits to avoid unexpected charges. The Free Tier Usage Dashboard helps track usage.
3. Consider Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
For predictable workloads, Reserved Instances (RIs) and Savings Plans provide discounts in exchange for a commitment to use AWS services for 1 or 3 years.
- — Tip: If you have ongoing, steady workloads (like a web server that runs 24/7), RIs or Savings Plans can reduce costs by up to 75%.
4. Take Advantage of Spot Instances
Spot Instances are available at a discount because they use AWS’s spare capacity. They’re ideal for fault-tolerant and flexible applications, such as batch processing and data analysis.
- — Tip: Use Spot Instances for workloads that can handle interruptions, such as background tasks. AWS also offers Spot Fleets for managing multiple Spot Instances and EC2 Auto Scaling to replace interrupted instances automatically.
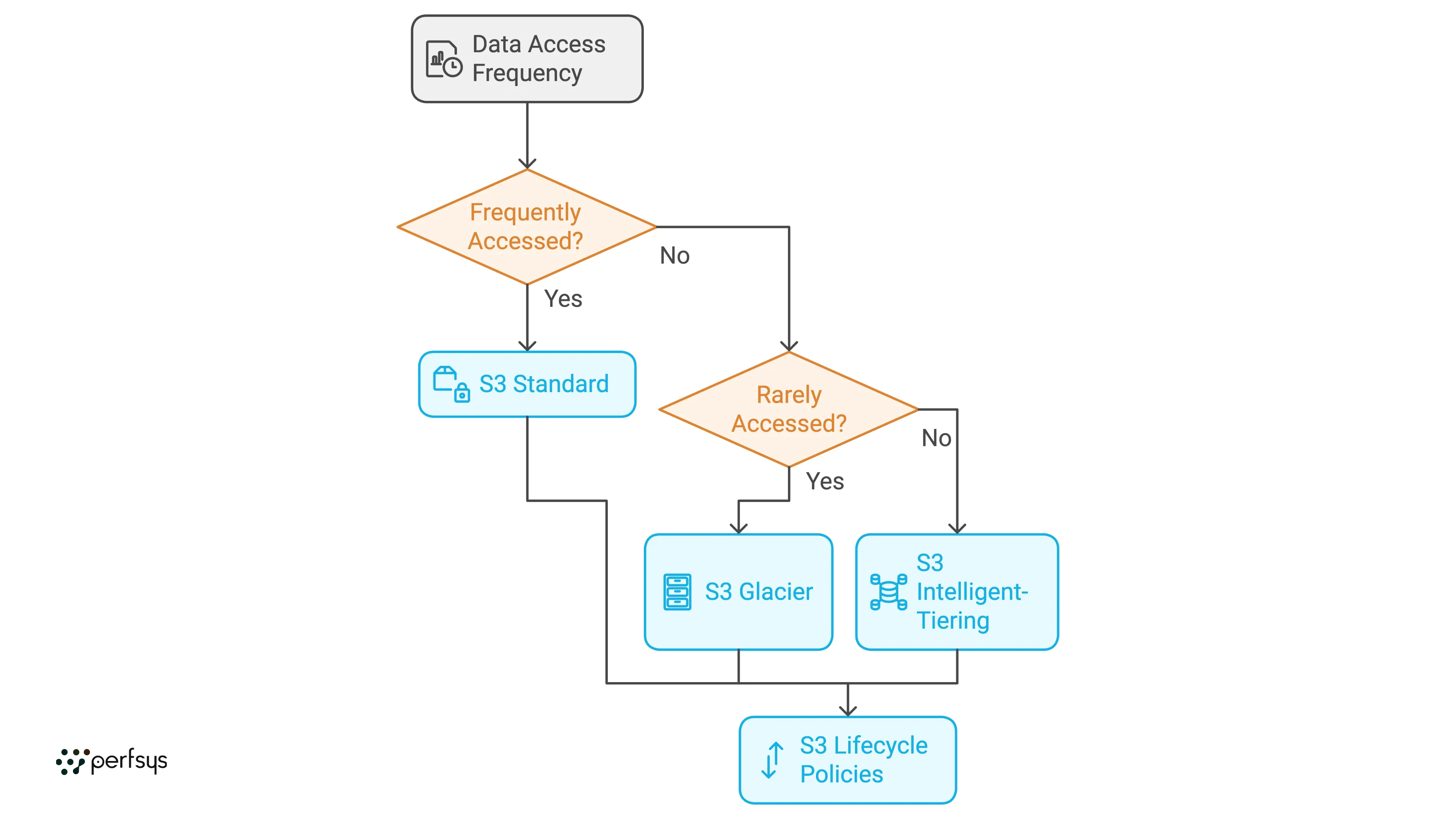
5. Optimize Storage Costs
AWS provides multiple storage classes within Amazon S3 to accommodate different data access patterns. Choose the right storage class based on how frequently you access your data:
-
— S3 Standard: For frequently accessed data.
-
— S3 Intelligent-Tiering: Automatically moves data to lower-cost tiers when access patterns change.
-
— S3 Glacier: Ideal for long-term, rarely accessed data (e.g., archives and backups).
-
— Tip: Use S3 Lifecycle Policies to automatically move data to cheaper storage classes based on access frequency.
6. Monitor and Manage Costs with AWS Cost Management Tools
AWS offers several tools to help track and control spending:
-
— AWS Cost Explorer: Visualize your AWS spending patterns and identify areas where you can reduce costs.
-
— Budgets and Alerts: Set budgets to receive alerts when costs exceed certain thresholds.
-
— Trusted Advisor: AWS Trusted Advisor provides recommendations to help you optimize your AWS environment, including cost-saving suggestions.
- — Tip: Set up alerts to stay on top of costs, and regularly review Trusted Advisor’s recommendations.
7. Use Lambda for Serverless Savings
If you’re looking to reduce server costs, consider AWS Lambda for serverless computing. Lambda only charges you for the compute time you use, making it a cost-effective option for applications with infrequent or variable workloads.
- — Tip: Use Lambda for on-demand processing or event-driven applications to save on server costs.
8. Right-Size Your Resources
AWS provides powerful resources, but over-provisioning can lead to unnecessary costs. Regularly review your usage to ensure you’re not paying for unused or oversized resources.
- — Tip: Use AWS Cost Explorer’s Rightsizing Recommendations to identify underutilized or idle resources, such as EC2 instances, and adjust them to more cost-efficient sizes.
9. Consider Data Transfer Costs
Data transfer charges apply when data is moved out of AWS to the internet or to other AWS Regions. Intra-Region transfers between Availability Zones are generally free, but cross-Region transfers can add up.
- — Tip: Minimize cross-Region transfers and host resources in the same Region to avoid data transfer fees. Use Amazon CloudFront for caching content closer to users to reduce bandwidth costs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is AWS Free Tier really free?
Yes, the Free Tier offers certain limits for free each month. However, exceeding these limits will incur charges, so it’s important to monitor usage.
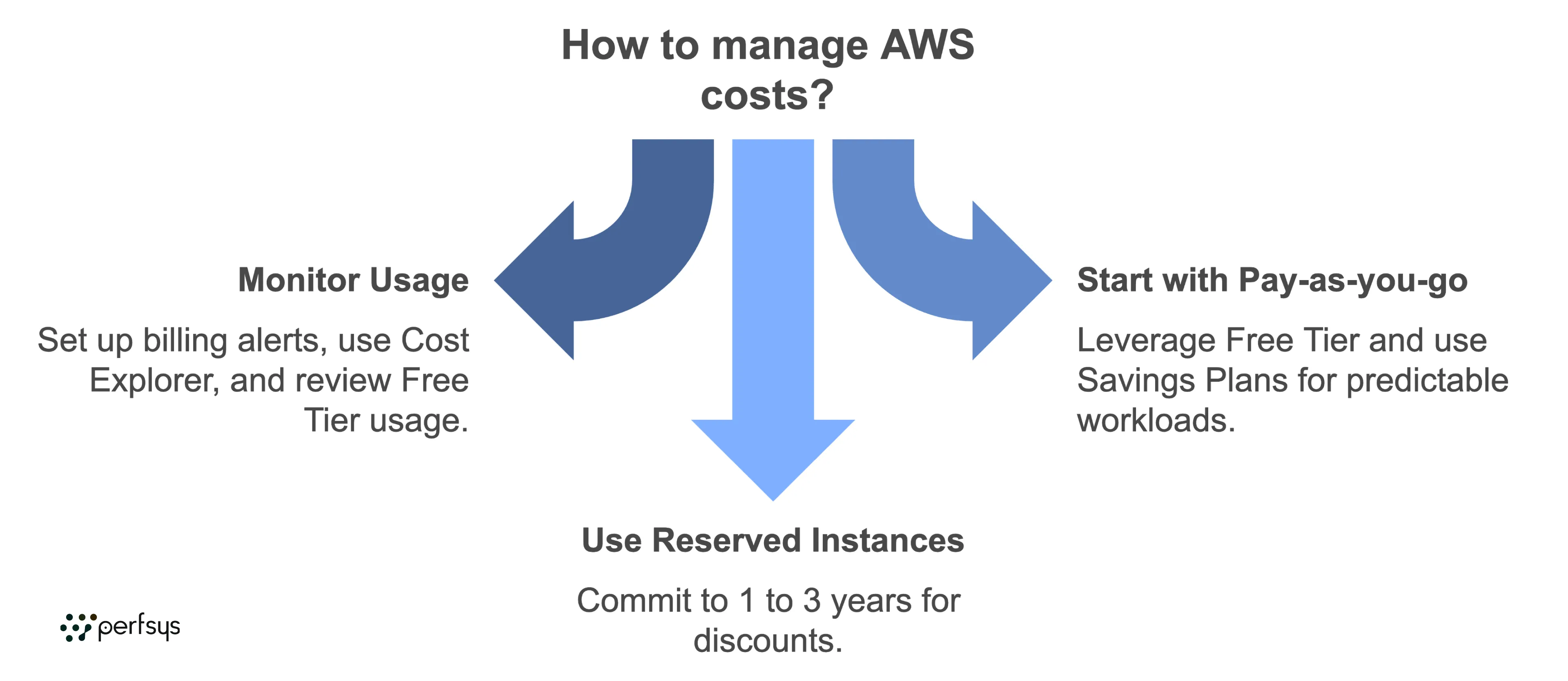
2. How can I avoid unexpected AWS charges?
Set up billing alerts, monitor usage in the Cost Explorer, and regularly review Free Tier usage. Always shut down unused resources to prevent extra costs.
3. What is the best way to manage costs for a small business?
Small businesses should start with pay-as-you-go options, leverage the Free Tier, and use Savings Plans for predictable workloads. Using serverless options like Lambda can also be cost-effective.
4. Are there discounts for long-term AWS usage?
Yes, AWS offers Reserved Instances and Savings Plans that provide discounts in exchange for a commitment of 1 to 3 years.
Conclusion
Managing AWS costs doesn’t have to be complicated. By understanding AWS pricing models, choosing the right instance types, and using AWS’s cost management tools, you can control your spending while still getting the performance you need.
Whether you’re just starting out or looking to optimize an existing setup, following these tips will help you save on your AWS cloud bill and make the most of your cloud investment.
