What is Cloud Computing? A Beginner’s Guide

Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses and individuals use technology, enabling access to vast computing resources without needing physical hardware. But what exactly is cloud computing, and how does it work? In this guide, we’ll break down the fundamentals of cloud computing, its benefits, and why it has become a key part of modern life.
What is Cloud Computing?
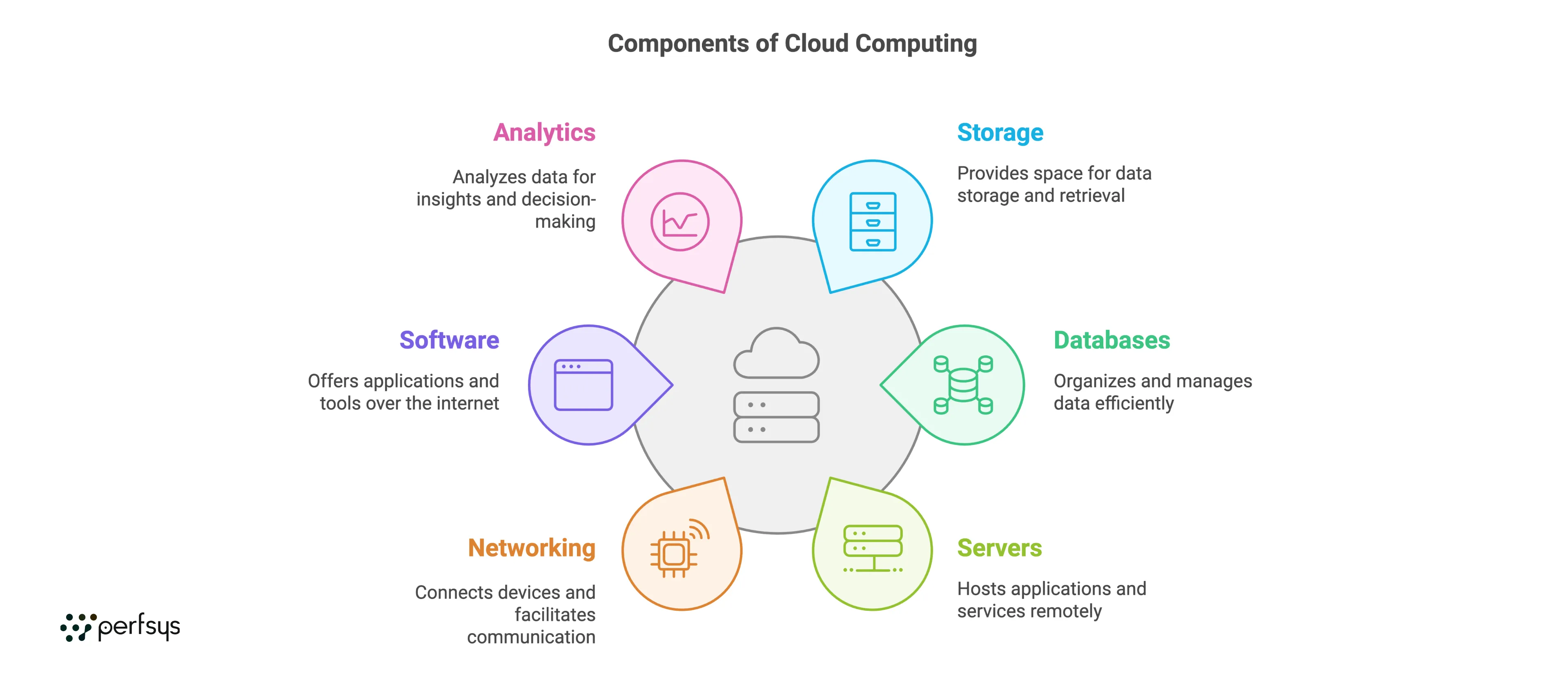
Cloud computing is the delivery of computing services — such as storage, databases, servers, networking, software, and analytics — over the internet (or “the cloud”) instead of on a local device or server. These services are hosted by cloud providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud, allowing users to access resources remotely on demand.
With cloud computing, users can:
-
— Store and access files and applications online from any device
-
— Process data at scale without purchasing and maintaining their own servers
-
— Scale resources up or down based on need, paying only for what they use
How Does Cloud Computing Work?
In cloud computing, data and applications are hosted on remote servers that users access over the internet. Cloud providers manage this infrastructure, handling the setup, maintenance, and security of servers so users can focus on their applications. When you upload a file to a cloud service or use an online app, the provider’s remote servers process, store, and secure your data.
Cloud providers typically use data centers located worldwide. These data centers are composed of powerful servers that offer resources on demand, ensuring high availability and reliability.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
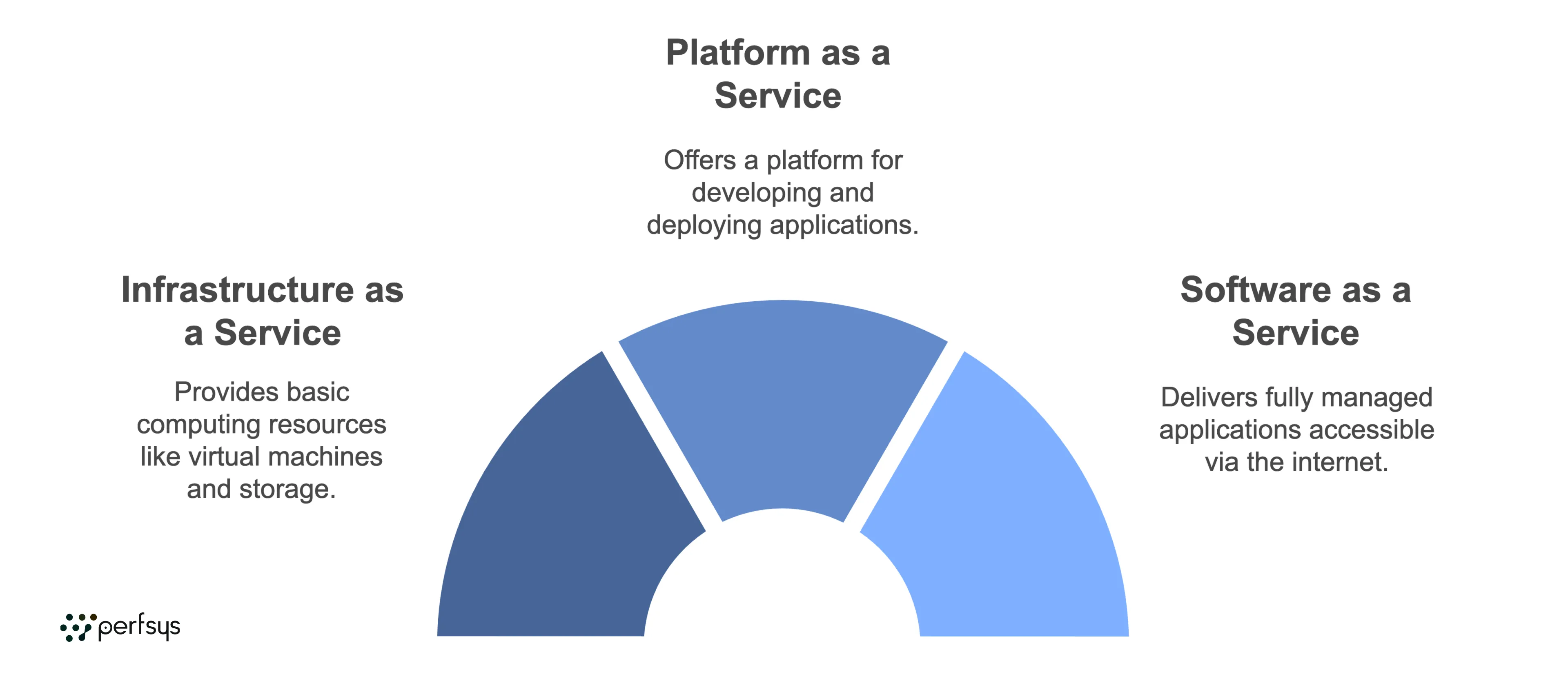
Cloud computing services generally fall into three categories: IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS. Each model provides different levels of control and flexibility.
1. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
What It Is: IaaS offers basic computing resources — like virtual machines, storage, and networks — on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Example: AWS EC2 (Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud) provides virtual servers that users can configure based on their needs.
Use Case: Ideal for businesses needing full control over their infrastructure to build custom solutions or run applications.
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
What It Is: PaaS provides a platform for developing, testing, and deploying applications without managing underlying infrastructure.
Example: Google App Engine lets developers deploy applications directly to the cloud, handling servers and storage for them.
Use Case: Suitable for developers who want to focus on coding and deploying applications without worrying about server management.
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
What It Is: SaaS delivers fully managed applications over the internet, available through a web browser or app.
Example: Microsoft Office 365 is a SaaS product that provides tools like Word and Excel online.
Use Case: Perfect for end users who want accessible, ready-to-use software without installation or updates.
Types of Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud computing also offers different deployment models based on who can access the services and where resources are located.
1. Public Cloud
Definition: Services are provided over the public internet and shared across multiple users.
Example: AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Pros: Cost-effective, scalable, and no maintenance required by the user.
2. Private Cloud
Definition: Exclusive cloud infrastructure dedicated to a single organization, often hosted on-site or by a private provider.
Example: VMware vSphere for private cloud virtualization.
Pros: Higher control and security, often used by enterprises with strict compliance requirements.
3. Hybrid Cloud
Definition: Combines public and private clouds, allowing data and applications to move between them.
Example: A company may store sensitive data in a private cloud while using a public cloud for less critical workloads.
Pros: Offers flexibility and control, enabling data to move across environments for optimized resource use.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
1. Cost Savings
Cloud computing reduces the need for businesses to purchase and maintain physical servers, software, and storage. The pay-as-you-go model means you only pay for what you use, with no upfront investment required.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
The cloud provides the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. Whether you’re running an e-commerce website during a holiday sale or processing large datasets, cloud resources can be adjusted automatically to meet your needs.
3. Accessibility and Mobility
Cloud services are accessible over the internet, meaning you can work from any device, anywhere. This makes it easy for teams to collaborate, share files, and access applications remotely.
4. Reliability
Cloud providers often have multiple data centers and redundant backups, ensuring data is always available. Many providers guarantee uptime through Service Level Agreements (SLAs), offering peace of mind for mission-critical applications.
5. Enhanced Security
Leading cloud providers invest in advanced security protocols and certifications to protect data, often offering tools like encryption, multi-factor authentication, and identity management. They also comply with regulatory standards, providing additional layers of security for sensitive data.
Common Examples of Cloud Computing in Daily Life
-
1. Email Services: Gmail, Outlook, and other email providers store messages in the cloud, accessible from any device.
-
2. File Storage and Sharing: Services like Google Drive, Dropbox, and iCloud store files in the cloud, enabling you to access documents and photos from any location.
-
3. Streaming Services: Platforms like Netflix and Spotify use cloud servers to stream video and music content globally, allowing users to enjoy media without local downloads.
-
4. Virtual Meetings: Zoom and Microsoft Teams rely on cloud computing for seamless video conferencing and file sharing.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is cloud computing secure?
Yes, reputable cloud providers use advanced security measures, including data encryption, identity management, and compliance certifications, to protect data.
2. Can I access my cloud data without an internet connection?
Typically, cloud services require an internet connection. Some services offer offline modes, but these are limited to certain applications and data.
3. How much does cloud computing cost?
Cloud computing costs vary based on usage, with pay-as-you-go models and discounts for long-term or high-volume commitments. Free tiers are often available for basic use.
4. Is cloud computing only for businesses?
No, cloud computing benefits individuals and businesses alike. Many people use cloud storage for personal files, email, and entertainment services like streaming.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is a powerful technology that offers convenience, scalability, and cost savings, enabling businesses and individuals to access computing resources from anywhere. Whether you’re storing personal files, collaborating on work projects, or running a large-scale application, the cloud provides the flexibility to meet your needs without the hassle of managing physical hardware.
As cloud technology continues to evolve, its impact will only grow, making it an essential part of modern computing. Ready to get started? Explore cloud services like AWS, Microsoft Azure, or Google Cloud to see how the cloud can benefit you!
