What is IoT? A Beginner’s Guide to the Internet of Things

The Internet of Things (IoT) is a term you may have heard, but what does it actually mean? In simple terms, IoT refers to the billions of devices worldwide that are connected to the internet, collecting and sharing data. These devices can range from everyday objects like smart home thermostats and wearable fitness trackers to advanced industrial equipment. This guide breaks down what IoT is, how it works, and why it’s transforming our daily lives and industries.
What is IoT?
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to a network of physical devices — also known as “smart devices” or “connected devices” — that use sensors, software, and the internet to collect and share data. By connecting to the internet, these devices can communicate with each other and with people, making life more convenient, efficient, and safe.
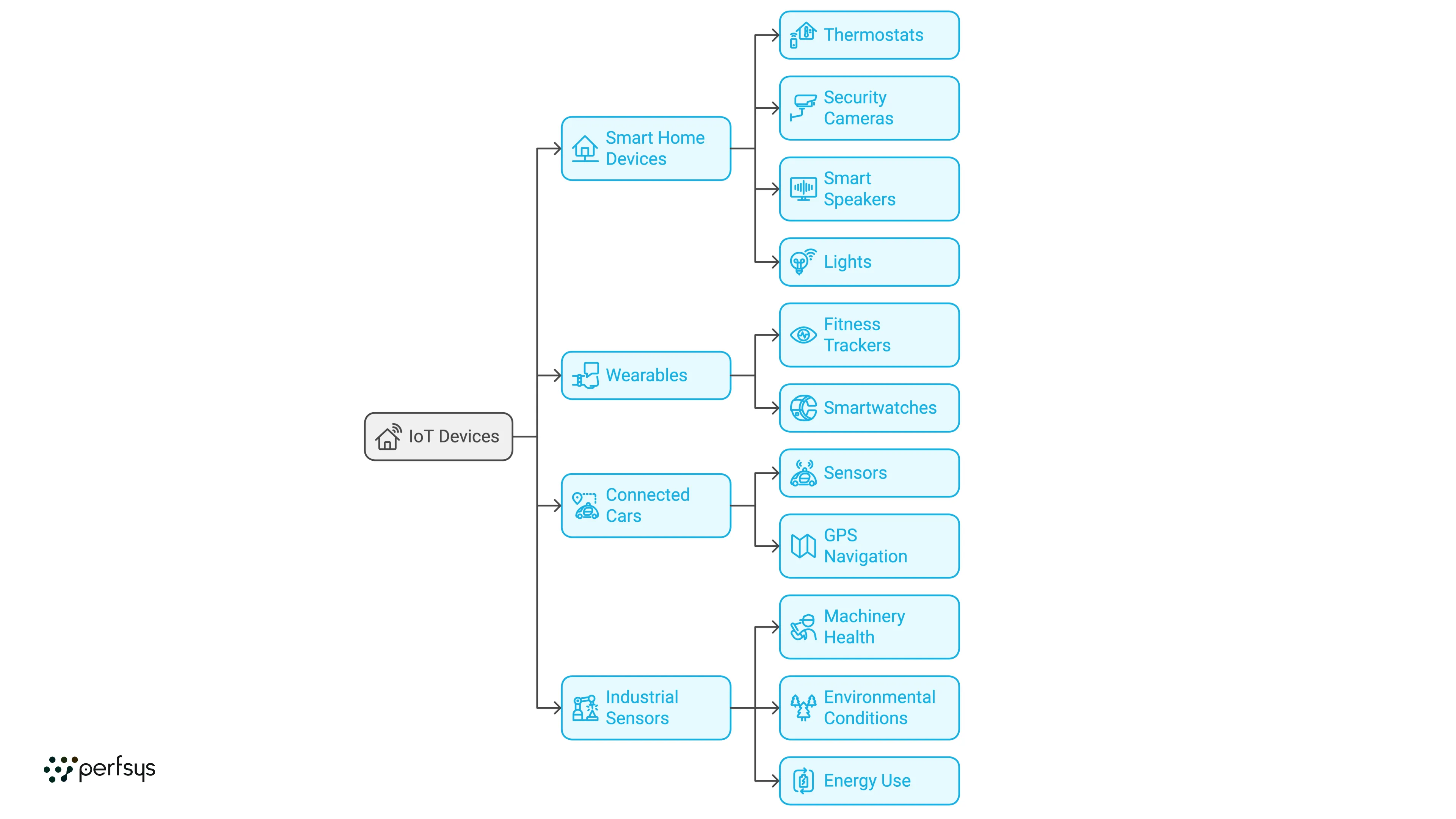
Examples of IoT devices:
-
— Smart Home Devices: Thermostats, security cameras, smart speakers (like Amazon Alexa or Google Home), and lights
-
— Wearables: Fitness trackers and smartwatches that monitor health and activity
-
— Connected Cars: Vehicles equipped with sensors that monitor performance and enable GPS navigation
-
— Industrial Sensors: Devices that track machinery health, environmental conditions, or energy use in factories
How Does IoT Work?
IoT devices work by:
-
1. Collecting Data: IoT devices have sensors that gather information. For example, a smart thermostat collects data on room temperature, while a fitness tracker monitors your heart rate.
-
2. Sending Data: The data collected by these devices is sent to the internet or to a central database (often referred to as the “cloud”) through Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks.
-
3. Processing Data: Once the data is stored, it can be analyzed to reveal patterns or insights. For instance, your smart thermostat learns your temperature preferences over time.
-
4. Taking Action: Many IoT devices can act based on the data. A smart thermostat, for example, can adjust the temperature automatically based on your preferences or energy-saving settings.
Why is IoT Important?
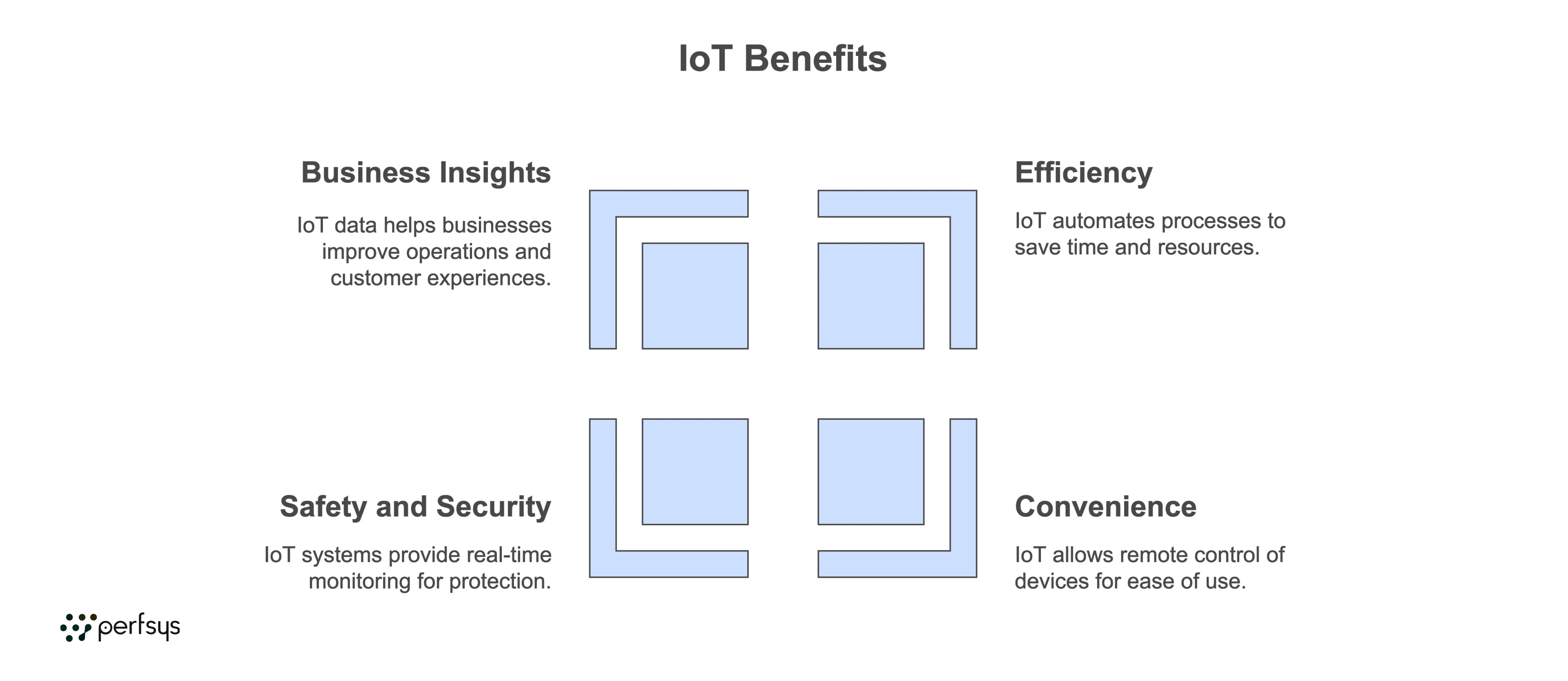
IoT is revolutionizing how we live and work by:
-
— Improving Efficiency: IoT can automate processes and save time. For example, smart appliances like washers or coffee makers can be scheduled to operate at optimal times.
-
— Enhancing Convenience: IoT enables remote control of devices, such as turning on lights or setting the home temperature from your smartphone.
-
— Increasing Safety and Security: IoT security systems with cameras, sensors, and alarms offer real-time monitoring and notifications to keep homes and workplaces secure.
-
— Driving Insights for Businesses: IoT data helps companies improve products, optimize operations, and provide better customer experiences.
Examples of IoT in Everyday Life
1. Smart Home Devices
Smart home technology includes devices like thermostats, light bulbs, and security cameras that can be controlled remotely. With these, users can:
-
— Adjust heating and cooling
-
— Turn lights on and off
-
— Monitor home security from a phone app
2. Wearable Technology
Wearables like fitness trackers, smartwatches, and health monitors track data such as steps taken, sleep patterns, and heart rate. They help individuals stay active, manage health, and connect with other apps for daily goals.
3. Connected Cars
Many new vehicles are equipped with IoT sensors that provide GPS directions, monitor tire pressure, and alert drivers to maintenance needs. Connected cars make driving safer, more efficient, and easier.
4. Industrial IoT (IIoT)
In industrial settings, IoT devices are used to monitor machinery, track inventory, and improve safety. For example, sensors on factory equipment can detect when a machine needs maintenance, reducing downtime.
How IoT Impacts Businesses
IoT enables businesses to:
-
— Optimize Operations: IoT sensors track manufacturing processes, warehouse conditions, and energy use, improving productivity and reducing waste.
-
— Enhance Customer Experience: Retail stores use IoT to manage inventory and personalize shopping experiences.
-
— Predict Maintenance Needs: IoT can predict when equipment might fail, allowing companies to perform maintenance before issues arise, saving time and costs.
IoT Security and Privacy Concerns
While IoT offers many benefits, it also brings challenges, especially in security and privacy:
-
— Security Risks: IoT devices can be vulnerable to cyberattacks if not properly secured. Hackers could potentially access personal data or control devices.
-
— Privacy Concerns: Since IoT devices collect a lot of personal data, users are often concerned about how their information is used and shared.
To mitigate risks, manufacturers and users should focus on secure network connections, regular software updates, and using strong passwords for IoT devices.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Is IoT only for high-tech devices?
No, IoT includes a wide range of devices, from simple sensors and smart home gadgets to complex industrial machines.
2. Can I control IoT devices without an internet connection?
Some IoT devices offer offline functionality, but many require an internet connection to access their full features and for remote control.
3. Are IoT devices safe to use?
IoT devices are generally safe, but security practices—such as strong passwords and updates—are essential to protect against cyber threats.
4. What are the biggest IoT trends today?
Popular trends include smart home automation, wearable health monitors, connected vehicles, and industrial IoT solutions for factories.
Conclusion
The Internet of Things (IoT) is transforming the way we live and work, connecting everyday devices to the internet to provide new levels of convenience, efficiency, and insight. From smart home devices to industrial sensors, IoT technology continues to expand, making our world more connected and interactive. As IoT evolves, it will play an even greater role in simplifying tasks, enhancing productivity, and driving innovation.
